



|
English Course |
|
MoRu |
TensesPresent Simple and Continuous Past Simple and Continuous Present Perfect Passive |
VerbsAuxiliary verbs do, be, and have Modal auxiliary verbsóMust, can, should, might, will, and would Full verbsóother verbs (play, run, help, think, want, go, see, eat, enjoy, live, die, swim, etc. Do, be and have can also be used as full verbs with their own meanings There are two forms of have in the present There are two forms of have in the present |
Auxiliary verbs and tenses- be and the continuous forms Be + verb +-ing is used to make continuous verb forms which describe activities in progress and temporary activities Heís washing his hair. (Present Continuous) They were going to work. (Past Continuous) Iíve been learning English for two years. (Present Perfect Continuous) Iíd like to be lying on the beach right now (Continuous Infinitive) - be and de passive voice Be + past participle is used to form the passive. Paper is made from Wood. (Presente Simple passive) My car was stolen yesterday. (Past Simple passive) The house has been redecorated. (Presente Perfect passive) This homework needs to be done tonight. (Passive infinitive) - have and de perfect forms Have + past participle is used to make perfect verb forms. He has worked in seven different conuntries. (presente Perfect) She was crying because she had had some bad news. (Past Perfect) Iíd like to have met Napoleon. (Perfect infinitive) |
Auxiliary verbs and negativesTo make a negatuvem add - nít to the auxiliary verb. If there is no auxiliary verb, use donít/doesnít/didnít.
It is possible to contract the auxiliaries be and have and use the uncontracted not Heís not playing today. (= He isnít playing today.) Weíre not going to Italy after all.(= We arenít going to Italy...) Iíve not read that book yet.(= I havenít read that book yet.) BUT† Iím not working. NOT† I amnít working |
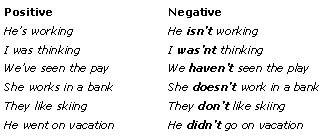
|
Question Sheís wearing jeans. You were Born in Mexico. Peterís been to China. I know you. He wants ice cream. They didnít go out. |
|
What is she wearing? Where were you born? Has Peter been to China? Do I know you? What does he want? Why didnít they go out? |
Auxiliary verbs and questionsTo make a question, invert the subject and the auxiliary verb. If there is no auxiliary verb, use do/does/did
There is usually no do/does/did in subject questions. Who wants ice cream?†††††††††††† What flavor ice cream do you want? What happened to your eyes?† What did you do to your eye? Who boke the window?††††††††††† How did you break the window? |
